We specialize in providing high-quality electroless nickel plating services to a wide range of industries. Our team of experienced professionals are dedicated to delivering exceptional results and meeting the unique needs of each of our clients. If you are looking for a reliable and experienced electroless nickel plating company, look no further than Tompkins Metal Finishing.

Pioneer offers many custom finishing solutions to make your products perform at the highest levels. We are experts in providing specialized finishes to improve the performance for your specific component parts. Whether your product design requirements include finishes to make your product resist corrosion, last longer, look better, slide more freely, bond securely to another material, or many...

At United Surface Finishing, we specialize in advanced metal finishing solutions with a strong focus on electroless nickel plating. We take pride in our ability to deliver precise, uniform coatings that enhance the performance and durability of metal components across demanding industries.

More Electroless Plating Companies
Electroless Plating: Process Overview, Applications, and Benefits
Electroless plating, also known as autocatalytic plating, is a highly sought-after metal finishing process that distinguishes itself from traditional electroplating by not requiring an external electrical current. Instead, the process relies on a controlled chemical reaction involving a reducing agent, frequently sodium hypophosphite or sodium borohydride, which triggers the deposition of a metallic layer onto the surface of a substrate or workpiece. The most common application involves the deposition of electroless nickel alloys, though other metals such as copper and silver can also be applied using this method.
How Does Electroless Plating Work?
The electroless plating process begins with meticulous preparation of the substrate to ensure optimal adhesion and uniform coverage. Proper surface pre-treatment is critical for high-quality results and involves a multi-stage cleaning protocol:
- Degreasing: Removes oils, grease, and organic contaminants from the substrate surface using solvents or alkaline cleaners.
- Acid Cleaning: Eliminates oxides, rust, and scale through immersion in acid baths.
- Water Rinsing: Multiple rinses between each cleaning step prevent cross-contamination and ensure a pristine surface.
If the cleaning process fails to remove all unwanted materials, the substrate cannot be properly plated. Any residual contaminants can lead to poor adhesion, blistering, or uneven deposit thickness. Once the substrate is thoroughly cleaned, it is activated—often with a catalyst such as palladium chloride for non-conductive materials—to initiate the chemical reduction process.
During the actual electroless deposition, the workpiece is immersed in a plating bath containing metal ions and the reducing agent. The chemical reaction deposits a uniform, adherent metal layer across all exposed surfaces—including complex geometries, blind holes, and internal recesses—without the need for electrical contacts or current distribution.
After the plating step, an anti-oxidation treatment may be applied to further enhance corrosion resistance, followed by additional rinsing and a drying or baking stage. Baking can improve the hardness and wear resistance of the plated layer, especially when high-phosphorus electroless nickel is used.
What Metals Can Be Electroless Plated?
While electroless nickel plating is the most prevalent, the process can also be used with other metals and alloys, including:
- Electroless copper plating (common in printed circuit board manufacturing)
- Electroless silver plating (used for electrical contacts and decorative finishes)
- Electroless cobalt and gold plating (specialized electronics and corrosion protection)
Each metal offers unique properties and performance characteristics, making electroless plating a versatile choice for a variety of industrial, commercial, and even decorative applications. Want to learn more about the types of metals suitable for electroless plating? Contact an expert today for tailored guidance.
Key Advantages of Electroless Plating
The electroless plating process offers several distinct advantages over traditional electrolytic (electroplating) methods:
- No Electrical Power Required: The process is powered by a chemical reaction, making it ideal for coating non-conductive surfaces and components with intricate shapes.
- Exceptional Uniformity: Achieves highly uniform plating thickness, even on complex geometries, internal surfaces, blind holes, and threads.
- Superior Corrosion Resistance: Especially with high-phosphorus electroless nickel, providing excellent protection in aggressive environments such as chemical processing, marine, and oil & gas industries.
- Improved Wear Resistance: The plated surface is hard and durable, reducing friction and extending component life in high-wear applications.
- Versatile Surface Finishes: Matte, semi-bright, and bright finishes are achievable, allowing for both functional and aesthetic benefits.
- Enhanced Lubricity: Electroless nickel coatings reduce friction, ideal for moving parts and assemblies.
- Dimensional Accuracy: The uniform deposit maintains tight tolerances, reducing the need for post-plating machining.
- Ability to Plate Non-Conductive Materials: With proper activation, plastics and ceramics can be metallized for EMI/RFI shielding or decorative purposes.
Common Industrial Applications of Electroless Plating
The unique properties and benefits of electroless plating make it indispensable across a wide range of industries, including:
- Automotive: Plating of engine components, fuel injection systems, pistons, gears, and hydraulic parts for wear and corrosion resistance.
- Aerospace & Defense: Protection of aircraft landing gear, actuators, and fasteners from harsh environmental exposure and friction.
- Electronics: Metallization of printed circuit boards (PCBs), connectors, and contacts for conductivity and solderability.
- Oil & Gas: Coating of valves, pumps, drill bits, and downhole tools to withstand corrosive and abrasive conditions.
- Medical Devices: Durable and biocompatible coatings on surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
- Industrial Machinery: Plating of rotors, drive shafts, rails, molds, and mechanical tools to extend service life and reduce maintenance.
- Consumer Products: Decorative and protective finishes on hardware, appliances, and jewelry.
Looking to improve the durability and performance of your parts? Request a custom electroless plating quote for your specific project requirements.
Types of Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless nickel plating is categorized based on the phosphorus content in the deposited alloy, each offering different characteristics:
- Low-Phosphorus (2-5% P): High hardness, good wear resistance, and excellent solderability. Suitable for electronics and precision components.
- Medium-Phosphorus (6-9% P): The most common type, balancing corrosion resistance with hardness. Widely used for general industrial applications.
- High-Phosphorus (10-13% P): Exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in acidic or chemical environments, but slightly lower hardness. Ideal for oil & gas, chemical processing, and marine uses.
Electroless Plating vs. Electroplating: Which Is Better?
When evaluating electroless plating vs. electroplating, key considerations include:
- Uniformity: Electroless plating produces a more even thickness on complex shapes and internal features.
- Material Compatibility: Electroless processes can deposit metal on plastics, ceramics, and other non-conductive substrates.
- Production Scale and Cost: While electroless plating can be more expensive due to chemical usage, it may reduce post-plating machining and scrap. Electroplating is often more cost-effective for high-volume, simple shapes.
- Performance Requirements: Electroless nickel offers superior corrosion and wear resistance for demanding environments.
Need help choosing the right metal finishing process for your manufacturing needs? Ask our technical team for a personalized recommendation.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Electroless Plating Services
When sourcing electroless plating services, consider these important decision factors to ensure optimal results:
- Substrate Material: Confirm compatibility and activation requirements for metals, plastics, or ceramics.
- Required Coating Thickness: Specify minimum and maximum thickness for functional or dimensional needs.
- Desired Surface Finish: Choose between matte, semi-bright, or bright finishes based on appearance and performance.
- Corrosion and Wear Resistance: Match phosphorus content to your application’s exposure level.
- Industry Standards and Certifications: Ensure compliance with relevant quality standards (e.g., ASTM B733, AMS 2404, ISO 4527).
- Turnaround Time and Batch Size: Align production schedules and order volumes with your supplier’s capabilities.
- Post-Plating Treatments: Ask about options such as heat treatment, passivation, or additional finishes like Teflon or PTFE for enhanced properties.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electroless Plating
- What is the typical thickness of electroless nickel plating?
Standard thickness ranges from 2.5 to 100 microns, depending on application. Precision parts may require tighter controls. - How long does electroless plating last?
Durability depends on coating thickness, type of substrate, and operating environment. Properly applied coatings can last for years in harsh industrial settings. - Can electroless plating be applied over other coatings?
Yes, with proper surface preparation, it can be deposited over many metals and some existing coatings. - Is electroless nickel plating environmentally friendly?
Modern processes minimize hazardous waste and comply with RoHS and REACH regulations, but always verify supplier environmental credentials.
Still have questions about electroless plating? Ask an expert.
Enhancing Performance with Advanced Electroless Plating Technologies
Recent innovations in advanced electroless plating include composite coatings that embed hard particles (such as PTFE, silicon carbide, or diamond) into the metal matrix. These electroless composite coatings significantly enhance wear resistance, friction reduction, and chemical stability. Applications range from high-performance automotive parts to aerospace components and medical tools requiring specialized surfaces.
Additionally, process automation, real-time bath monitoring, and eco-friendly chemistries are transforming the industry—delivering higher consistency, reduced downtime, and improved environmental compliance.
Want to discover how advanced electroless plating can solve your toughest engineering challenges? Explore our latest technologies or schedule a consultation with our process development team.
Why Choose Electroless Plating for Your Next Project?
Whether you need to enhance the corrosion resistance of critical components, improve surface hardness, or achieve a flawless decorative finish, electroless plating offers unmatched versatility and performance. Key reasons to choose this advanced surface finishing technology include:
- Ability to plate complex shapes and internal features uniformly
- Superior protection against wear, corrosion, and chemical attack
- Compatibility with a wide range of substrate materials
- Customizable finishes and functional properties
- Proven success in demanding industries worldwide
Ready to improve your product’s performance and longevity? Request a quote or contact our technical team today to discuss your specific requirements.
Looking for more information on electroless plating services, capabilities, or technical data? Connect with an expert for personalized assistance.





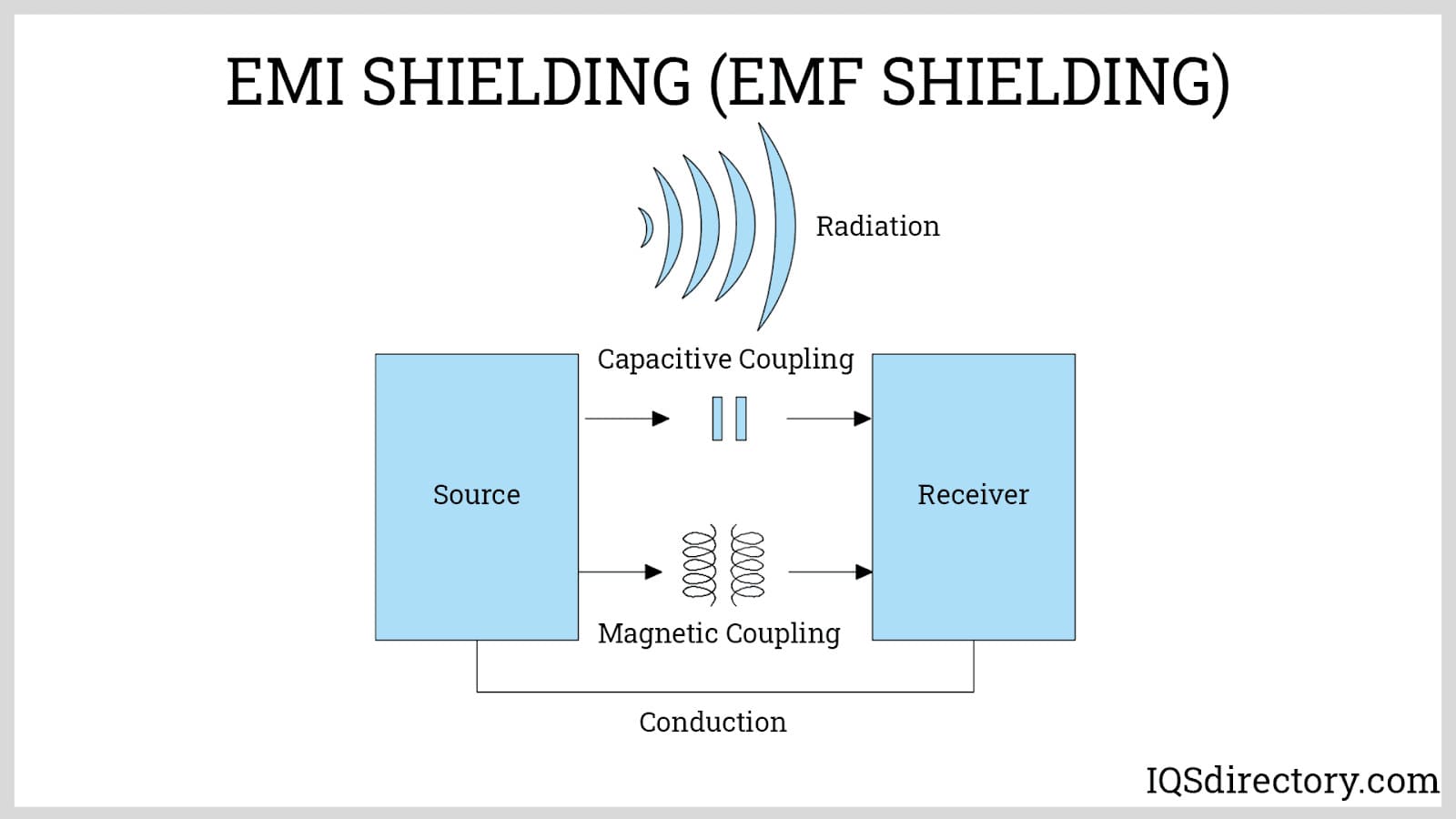
 Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum Anodizing EDM
EDM Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless Nickel Plating EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Heat Treating
Heat Treating Metal Coating Services
Metal Coating Services Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services