Electroless nickel plating is a process that uses auto-catalytic chemical reactions to create a layer of nickel alloy to coat a metal or plastic object. The process works in such a way that the nickel alloy coating deposits directly onto the substrate as the chemical reaction creates it. Read More…
We specialize in providing high-quality electroless nickel plating services to a wide range of industries. Our team of experienced professionals are dedicated to delivering exceptional results and meeting the unique needs of each of our clients. If you are looking for a reliable and experienced electroless nickel plating company, look no further than Tompkins Metal Finishing.

Pioneer offers many custom finishing solutions to make your products perform at the highest levels. We are experts in providing specialized finishes to improve the performance for your specific component parts. Whether your product design requirements include finishes to make your product resist corrosion, last longer, look better, slide more freely, bond securely to another material, or many...

At United Surface Finishing, we specialize in advanced metal finishing solutions with a strong focus on electroless nickel plating. We take pride in our ability to deliver precise, uniform coatings that enhance the performance and durability of metal components across demanding industries.

More Electroless Nickel Plating Companies
Electroless nickel plating is an advanced metal finishing process that utilizes auto-catalytic chemical reactions to deposit a uniform nickel alloy layer onto a wide variety of substrates, including metals and plastics. Unlike traditional electroplating, which requires an electrical current to facilitate the metal plating process, electroless plating relies solely on chemical reduction, making it a highly versatile and reliable coating method for complex shapes and intricate geometries.
During electroless nickel plating, the nickel alloy forms a protective coating as the chemical reaction progresses, resulting in a dense, even, and adherent layer. This process provides significant engineering benefits and is a sought-after solution for industries requiring superior corrosion resistance, wear protection, and functional surface enhancements.
Electroless nickel plating is also recognized by industry professionals through several synonymous terms: electroless nickel coating, EN plating, E/Ni plating, chemical nickel plating, autocatalytic nickel plating, autocatalytic plating, and autocatalytic coating. More broadly, electroless plating can be extended to other metals such as copper, gold, and silver, offering a diverse range of technical and aesthetic applications.
Applications: Where Is Electroless Nickel Plating Used?
Electroless nickel plating is a specialized service frequently offered by surface finishing companies and precision manufacturers for a vast array of industrial and commercial products. This process is tailored for sectors where high-performance coatings are vital, including:
- Chemical processing plants
- Oil & gas and petroleum industries
- Automotive manufacturing and parts suppliers
- Aerospace and aviation engineering
- Electronics and semiconductor production
- Military and defense contractors
- Household appliance and fixture manufacturers
- Food processing and packaging equipment
- General manufacturing and OEMs
- Jewelry and luxury goods
Industries choose electroless nickel plating for its unmatched combination of properties and protection. The nickel coating not only enhances durability and wear resistance, but also provides robust corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Its uniformity ensures consistent coverage—even on threaded, recessed, or complex parts—while delivering a smooth, attractive finish. For electronics, electroless nickel plating offers electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and enhances conductivity, making it indispensable for connectors, circuit boards, and sensitive components. In aerospace and automotive applications, high-phosphorus electroless nickel layers offer increased hardness, chemical resistivity, and lubricity. In addition, electroless nickel coatings maintain cleanliness, are non-magnetic (in certain formulations), and can be customized for specific friction, hardness, and appearance requirements.
Products Treated: What Can Be Electroless Nickel Plated?
Looking for examples of products that benefit from electroless nickel plating? Explore how this process is used in diverse industries to enhance performance, extend lifespan, and add value:
- Chemical: turbine blades, pressure vessels, hydraulic components, chemical reactors, process valves
- Petroleum: fuel rails, oilfield valves, downhole drilling tools, pump components
- Automotive: brake pistons, drive shafts, mufflers, rotors, camshafts, power transmission gears, fuel injectors, engine blocks
- Aerospace: propellers, engine shafts, engine mounts, compressor blades, landing gear equipment, actuators, fasteners
- Electronics: connectors, hard drive disks, wire terminals, printed circuit boards (PCBs), semiconductors, RF shielding enclosures
- Military and defense: firearms and weapons, optical mirrors, fuse assemblies, guidance systems, armor plating
- Household: bathroom fixtures, door knobs, door and cabinet fasteners, stainless steel utensils, kitchen appliances
- Food prep: grills, molds, canning machines, mixers, conveyor belts, food service equipment
- Manufacturing: pipes, tools, gears, fasteners, machine components, dies, molds
- Jewelry: diamond turning, other optical surfaces, decorative pieces, luxury watch components
Want to know if your product or part is a good candidate for electroless nickel plating? Ask an expert plating company about your application’s requirements and get recommendations for optimal coating solutions.
History of Electroless Nickel Plating
The discovery of electroless nickel plating was a pivotal moment in the evolution of industrial surface treatments. Rather than being purposefully invented, the process was discovered serendipitously between 1841 and 1845 by Alsatian French chemist Adolphe Wurtz, while he was investigating hypophosphorous acid and its chemical properties. Wurtz observed that immersing nickel-phosphorous compounds in a chemical reduction bath resulted in spontaneous nickel ion deposition onto a substrate—a phenomenon that would later be harnessed for modern metal finishing.
Although Wurtz soon shifted his focus to other fields, his discovery laid the groundwork for future innovation. In 1916, American chemist F.A. Roux secured the first U.S. patent for electroless nickel coating, describing the process as “spontaneous and complete” nickel deposition. Despite this milestone, electroless nickel plating remained a niche process for decades.
Significant advancements came in the 1940s, when Grace Riddell and Abner Brenner developed a method to deposit nickel-tungsten onto the inner surfaces of tubes. Their process, initially called “electrodeless plating,” received a patent in 1950 and was later refined to distinguish it from Roux’s earlier work. The method remained classified for military use during World War II, only becoming widely available to civilian industries after 1963.
Throughout the 20th century, research and innovation expanded the range of materials and composites that could be deposited using electroless plating. Pioneering work by K. Parker in the 1970s explored advanced composite coatings such as Teflon (PTFE), boron carbide, tungsten carbide, and others, further broadening the process’s utility and performance. Today, electroless nickel plating is an indispensable technology in electronics, aerospace, automotive, and many other sectors—enabling the creation of components with precisely engineered surfaces, enhanced durability, and exceptional reliability.
Materials: What Metals Can Be Electroless Plated?
While electroless plating is most commonly associated with nickel alloys, the process can be adapted to deposit a variety of other metals and alloys, each offering specific advantages for different applications. Common electroless plating metals include:
- Nickel (with phosphorus or boron alloying)
- Gold
- Silver
- Tin
- Copper
- Zinc
- Chrome
- Cadmium
- Palladium
- Rhodium
Of these, nickel, gold, copper, silver, and palladium are the most widely used for high-performance and decorative applications. Each metal brings its own unique set of properties—for example, gold is valued for its corrosion resistance and conductivity in electronics, while copper enhances electrical performance in connectors and circuit boards.
Looking to compare electroless plating vs. electroplating? Electroplating, which uses direct electrical current, is also used for metals like tin, zinc, chrome, cadmium, and rhodium, but may not offer the same uniformity or coverage on complex part geometries.
Gold plating is often used in the electronics industry to provide a corrosion-resistant, highly conductive layer over base metals. Silver plating is a more cost-effective alternative but is prone to tarnishing in humid environments, which may impact conductivity and appearance over time. Tin plating, especially when combined with copper, is valued for its excellent electrical properties and is widely used in connector manufacturing.
Zinc plating is essential for protecting steel and iron parts from oxidation and corrosion, especially in automotive and industrial settings. Chrome plating delivers a high-gloss, polished finish but is more expensive and energy-intensive. Palladium, though costly, is prized for its bath stability and is used in niche applications where performance is critical. Rhodium plating is primarily used in jewelry to enhance luster and durability. Cadmium plating, while effective, is restricted due to environmental and health concerns.
When discussing electroless nickel plating, manufacturers often use nickel-phosphorus alloys with different phosphorus concentrations, classified as:
- Low phosphorus (less than 5%): Offers high hardness (up to 60 RC), superior solderability, minimal electrical resistance, and excellent resistance to alkaline environments. The crystalline deposit structure is ideal for electronics and high-wear parts.
- Medium phosphorus (5%–9%): Balances hardness and corrosion resistance, provides the most visually appealing finish, and forms either a crystalline or mixed amorphous structure, making it suitable for decorative and industrial uses.
- High phosphorus (10%–13%): Delivers maximum corrosion protection, particularly in acidic environments. The amorphous structure enhances resistance and, when heat-treated, achieves hardness above 65 RC, making it suitable for harsh chemical and marine applications.
Wondering which plating alloy best suits your needs? Contact a plating specialist to discuss the advantages of low, medium, and high phosphorus electroless nickel coatings for your specific application.
Process Details: How Does Electroless Nickel Plating Work?
Electroless nickel plating is a multi-step chemical process engineered to deliver a uniform, high-quality nickel coating on a wide range of substrates. Here’s an in-depth look at each stage:
1. Surface Preparation
The process begins with meticulous cleaning to remove dirt, grease, oxides, and other contaminants. Surface preparation may include degreasing, alkaline cleaning, acid etching, and abrasive blasting. Proper preparation is vital to ensure optimal adhesion and prevent defects such as peeling or flaking.
2. Activation
After cleaning, the substrate is activated to create nucleation sites for nickel deposition. This may involve immersion in acidic solutions, sensitizing agents like palladium chloride, or proprietary activation baths, tailored to the base material. Activation ensures a uniform and adherent nickel coating.
3. Plating Bath Preparation
The core of the process is the plating bath, a carefully controlled solution containing nickel ions, reducing agents (typically sodium hypophosphite), stabilizers, complexors, and other essential chemicals. The reducing agent converts nickel ions into metallic nickel, depositing them onto the activated surface. For specialized applications, borohydride-based solutions may be used to achieve unique coating properties.
4. Immersion in the Plating Bath
The activated substrate is immersed in the plating bath, where the autocatalytic reaction occurs. Unlike electroplating, no external current is required; the chemical reaction itself drives the deposition of nickel atoms onto the substrate, building up a consistent layer.
5. Autocatalytic Deposition
The process is self-perpetuating—each new layer of nickel serves as a catalyst for further deposition. This ensures the nickel coating grows evenly and consistently until the desired thickness is reached, regardless of the part’s shape or geometry.
6. Controlling Plating Parameters
Critical process parameters—such as bath temperature, pH, nickel ion concentration, agitation, and reducing agent levels—are continuously monitored and adjusted. Tight control ensures uniform coating thickness, optimal hardness, and consistent quality.
7. Rinsing and Drying
Once plating is complete, the part is thoroughly rinsed to remove residual chemicals, then dried to prevent water spots or corrosion. Additional post-treatments, such as heat treatment, passivation, or specialized coatings, may be applied to further enhance properties.
Want a step-by-step guide to optimizing the electroless nickel plating process for your parts? Ask a technical consultant for process audits and quality control best practices.
Benefits: Why Choose Electroless Nickel Plating?
Electroless nickel plating offers a host of benefits over other metal finishing processes, including:
- Superior Corrosion and Wear Resistance: Protects parts from rust, chemical attack, and abrasion—even in harsh environments.
- Uniform Coating Thickness: Ensures complete, even coverage on complex geometries, blind holes, internal surfaces, and threads.
- Improved Hardness and Surface Properties: Enhances component durability, extends service life, and reduces maintenance costs.
- Electrical and Thermal Conductivity: Essential for electronics, connectors, and heat-sensitive components.
- Customizable Properties: Tailor hardness, lubricity, and appearance by adjusting bath formulation and phosphorus content.
- No Need for Electric Current: Simplifies setup, reduces risk of defects, and eliminates concerns over current density or part geometry.
- Cost-Effective for Batch and Complex Parts: Ideal for high-volume or intricate components where electroplating would be impractical or cost-prohibitive.
- Decorative Appeal: Provides a bright, smooth, and aesthetically pleasing metal finish suitable for consumer goods and luxury items.
Ready to maximize the longevity and reliability of your parts? Request a quote for electroless nickel plating services from a certified provider near you.
Considerations: Making the Right Plating Choice
Choosing the optimal electroless nickel plating process for your application involves careful evaluation of several key factors:
- Substrate Material Compatibility: Different base materials (steel, aluminum, copper, plastics) require specific cleaning and activation methods to ensure adhesion.
- Desired Coating Properties: Assess whether you need maximum corrosion resistance, high surface hardness, solderability, or special friction characteristics.
- Plating Thickness and Tolerances: Define the required thickness to meet functional or dimensional specifications.
- Operating Environment: Consider exposure to chemicals, temperature extremes, moisture, and abrasion.
- Post-Plating Requirements: Determine if additional treatments (heat treatment, passivation, polishing) are needed to meet performance standards.
- Quality Assurance: Insist on thorough inspections, including thickness measurements, adhesion testing, and surface analysis.
- Packaging and Storage: Ensure components are handled and packed to maintain coating integrity during transit and storage.
- Environmental and Regulatory Compliance: Select processes and suppliers that meet industry and environmental standards, especially for applications in aerospace, defense, or medical devices.
Not sure which plating solution meets your industry’s specifications? Explore our resource library or contact a technical advisor for tailored recommendations and case studies.
Advantages Over Similar Metal Finishing Processes
How does electroless nickel plating compare to other metal finishing technologies? Here’s an overview:
- Electroplating: Relies on direct current to deposit metal onto a substrate. While useful for some applications, it struggles with uniform coverage on intricate or complex parts and requires expensive current control systems.
- Electrochemical Deposition: Similar to electroplating but typically used for copper, gold, or other metals. Again, it’s limited by the need for electrical current and may result in uneven coatings.
- Electroless Nickel Plating: Delivers unmatched coating uniformity, even on the most challenging geometries. Its autocatalytic nature eliminates the need for external power, reducing setup time and minimizing risk of defects. Versatile bath formulations allow for precise tuning of coating properties, making it the preferred solution for demanding engineering and industrial applications.
In summary, electroless nickel plating is the go-to choice for applications requiring high-performance, consistent, and reliable metal coatings—especially where part complexity, uniformity, and corrosion resistance are paramount.
How to Select the Best Electroless Nickel Plating Provider
With so many providers available, how do you ensure you’re choosing a top-tier electroless nickel plating company for your project?
- Review Track Records: Look for providers with proven results, satisfied clients, and robust quality control systems.
- Define Application Requirements: Before reaching out, create a detailed list of your needs—include substrate, required properties, budget, lead time, and special considerations.
- Shortlist Trusted Suppliers: Use curated listings (like those on this site) to identify reputable manufacturers with expertise in your industry.
- Request Quotes and Technical Guidance: Contact 3–4 top candidates to discuss your application, plating options, and pricing.
- Compare Solutions: Evaluate proposals based on capability, turnaround time, cost, and value-added services (such as lab testing or custom formulations).
- Verify Certifications: Ensure the provider meets relevant standards (ISO, ASTM, Nadcap, or industry-specific accreditations).
- Ask About Support: Inquire about process audits, technical troubleshooting, and ongoing quality assurance.
Ready to get started? Browse our list of leading electroless nickel plating companies or contact a technical expert for personalized advice and fast, accurate quotes.
Frequently Asked Questions About Electroless Nickel Plating
What is electroless nickel plating used for?
Electroless nickel plating is used to improve corrosion resistance, wear protection, and surface properties of parts in industries such as aerospace, automotive, electronics, oil & gas, and food processing. It is especially valuable for complex or irregularly shaped components.
Can plastic parts be electroless nickel plated?
Yes, with proper surface preparation and activation, many types of plastics can be coated using electroless nickel plating, expanding the process’s use in lightweight and composite components.
How thick can electroless nickel plating be applied?
Typical thicknesses range from 0.0001″ (2.5 µm) up to 0.005″ (125 µm) or more, depending on application requirements.
How does electroless nickel plating compare to hard chrome plating?
While hard chrome offers superior hardness and a mirror-like finish, electroless nickel provides better uniformity, corrosion resistance, and is more versatile for delicate or complex parts.
Is electroless nickel plating environmentally friendly?
Modern processes are engineered to minimize hazardous byproducts and comply with environmental standards, but it’s important to partner with suppliers who follow best practices for waste treatment and regulatory compliance.
How do I get a quote or technical consultation?
You can browse our listings or contact us directly for personalized assistance.
Conclusion: The Value of Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless nickel plating is a cornerstone of modern surface engineering, combining chemical innovation with practical benefits for countless industries. Its ability to provide uniform, durable, and corrosion-resistant coatings—without the complexity of electrical current—makes it the ideal choice for manufacturers, engineers, and designers seeking reliable metal finishing. Whether you’re aiming to increase component lifespan, improve product performance, or meet stringent industry standards, partnering with an experienced electroless nickel plating provider is key to achieving success.
Ready to take the next step? Find a qualified electroless nickel plating company or get expert answers to your technical questions today!



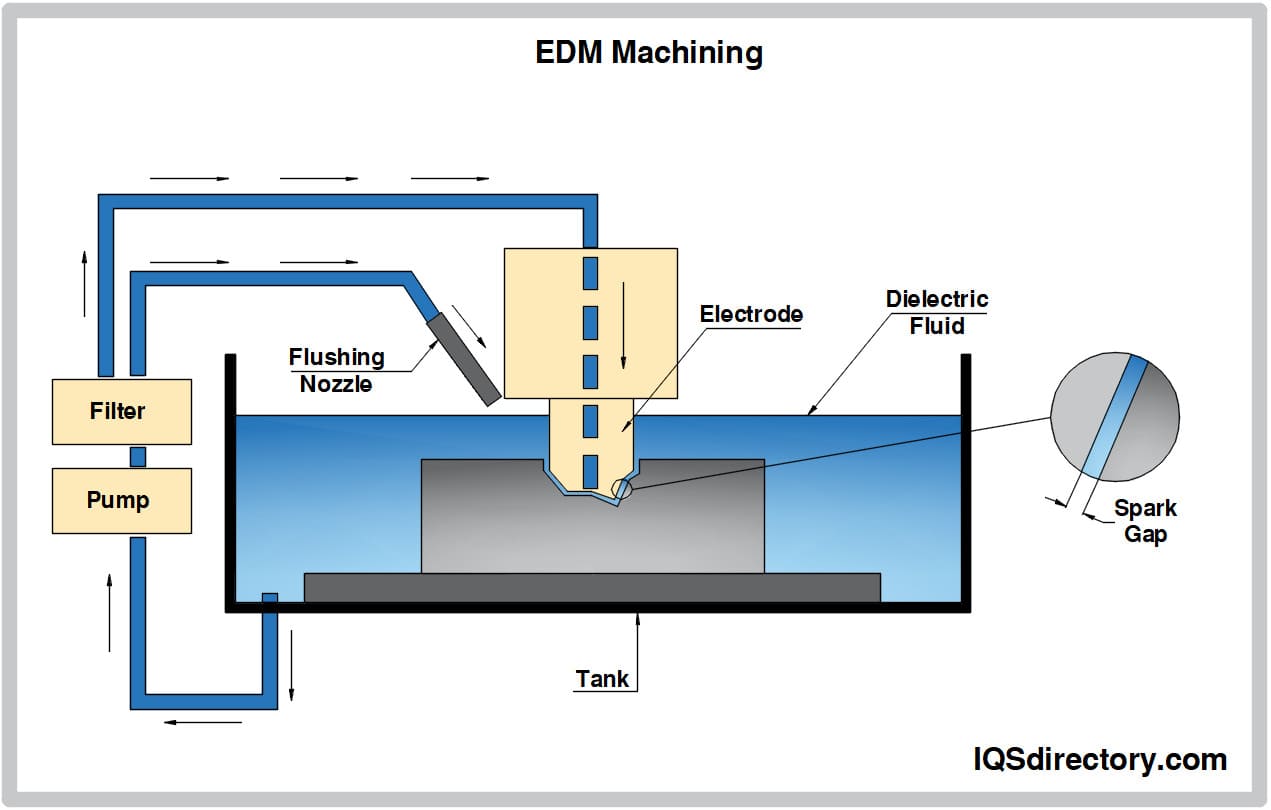
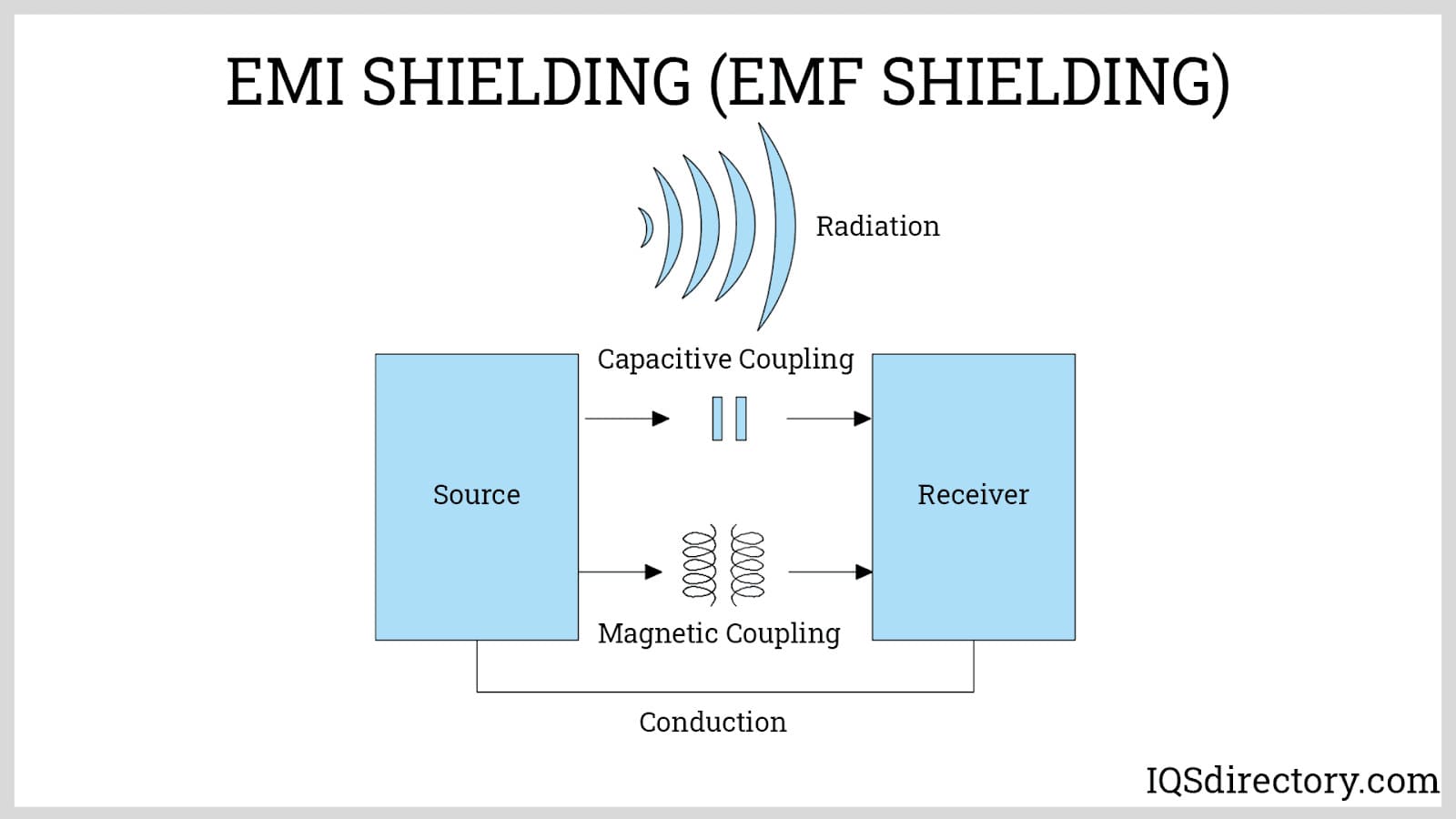
 Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum Anodizing EDM
EDM Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless Nickel Plating EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Heat Treating
Heat Treating Metal Coating Services
Metal Coating Services Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services